Content
- Accounting formulas for businesses
- The Creative Agency’s Guide to Cash Flow Management
- The basic accounting equation
- Accounting basics for small businesses
- Final Thoughts On Calculating The Equation
- Relax—run payroll in just 3 easy steps!
- What Is Shareholders’ Equity in the Accounting Equation?
- Expanded accounting equation

In other words, the shareholders or partners own the remainder of assets once all of the liabilities are paid off. This decreases the inventory account and creates a cost of goods sold expense that https://www.bookstime.com/ appears as a decrease in the income account. Equity is simply the difference between assets and liabilities. The owner has positive equity only to the extent that assets exceed liabilities.
It is the standard for financial reporting, and it is the basis for double-entry accounting. Without the balance sheet equation, you cannot accurately read your balance sheet or understand your financial statements. In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation.

We saved more than $1 million on our spend in the first year and just recently identified an opportunity to save about $10,000 every month on recurring expenses with PLANERGY. The net assets part of this equation is comprised of unrestricted and restricted net assets.
Accounting formulas for businesses
To record capital contribution as the owners invest in the business. The total left side and the total right side of each accounting transaction must balance. However, the asset Cash increased by the same amount that the asset Accounts Receivable decreased. Therefore, the total amount of assets will not change.

This statement is also prepared in the same conjunction as the balance sheet. Accounts ReceivableAccounts receivables is the money owed to a business by clients for which the business has given services or delivered a product but has not yet collected payment. They are categorized as current assets on the balance sheet as the payments expected within a year. It is shown as the part of owner’s equity in the liability side of the balance sheet of the company. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income , AOCIL, is a component of shareholders’ equity besides contributed capital and retained earnings. In this expanded accounting equation, CC, the Contributed Capital or paid-in capital, represents Share Capital. Retained Earnings is Beginning Retained Earnings + Revenue – Expenses – Dividends – Stock Repurchases.
The Creative Agency’s Guide to Cash Flow Management
Again, your assets should equal liabilities plus equity. Add the $10,000 startup equity from the first example to the $500 sales equity in example three.
- The equation summarizes one result of using making double-entry debits and credits correctly.
- However, the asset Equipment increased by the same amount that the asset Cash decreased.
- The transaction should also be marked as a reduction of capital due to the spending of cash.
- We want to increase the asset Truck and decrease the asset cash for $8,500.
- If both ledgers of your balance sheet don’t match, there may be an error.
The accounting balance sheet formula makes sure your balance sheet stays balanced. If you’re a small business owner who would prefer to monitor your company’s cash flow with your own two eyes, there are financial accounting equations that you should be familiar with.
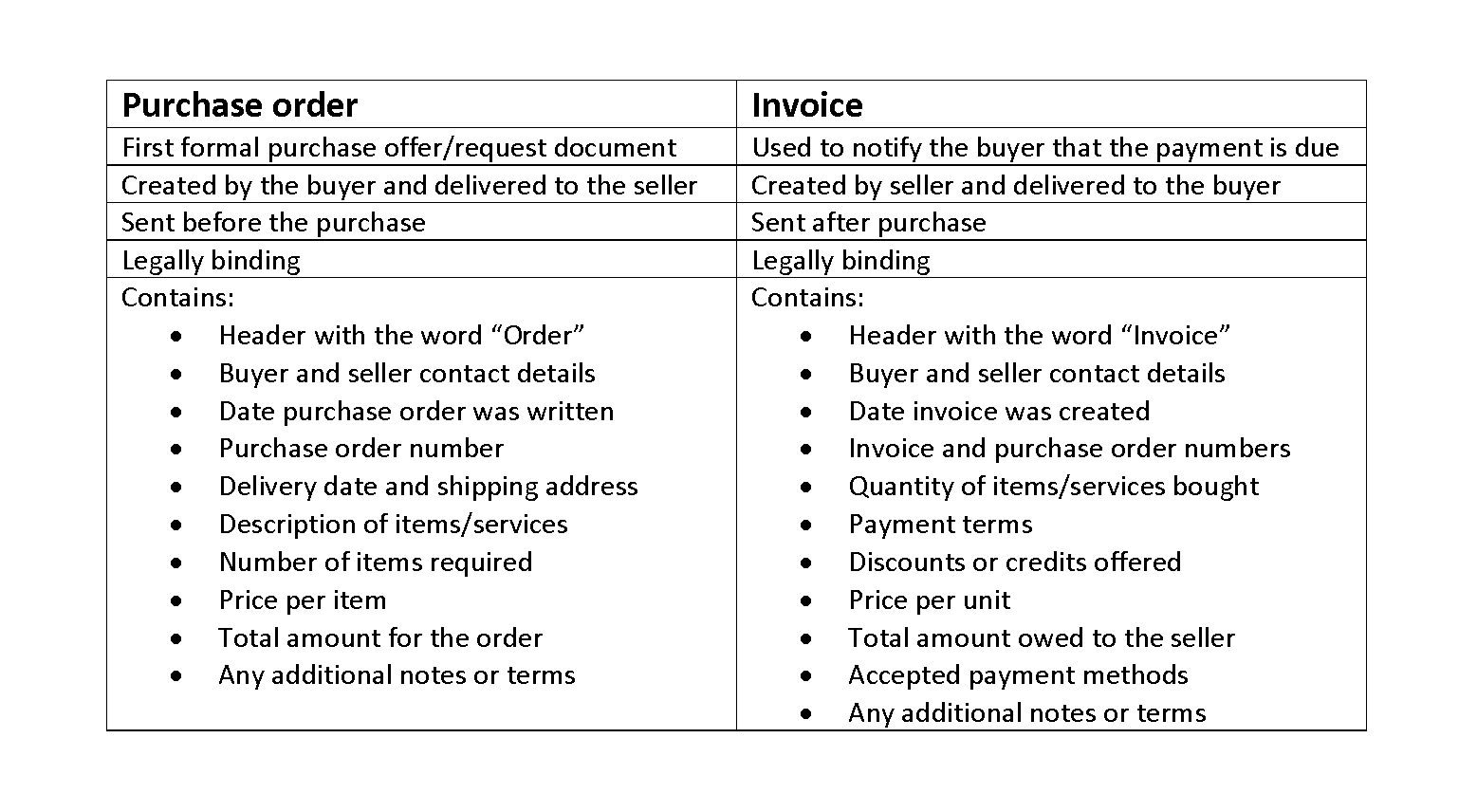
The basic accounting equation
These fundamental accounting equations are rather broad, meaning they can apply to a wide array of businesses. A company’s quarterly and annual reports are basically derived directly from the accounting equations used in bookkeeping practices. These equations, entered in a business’s general ledger, will provide the material that eventually makes up the foundation of a business’s financial statements. This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments. In order to make sure that the accounts of a company are balanced, the total assets must equal the sum of the total of all liabilities and owner’s equity. To see if everything is balanced, the totals are simply plugged in to the accounting equation. Once the math is done, if one side is equal to the other, then the accounts are balanced.
Withdrew inventory for personal purpose by owner of worth Rs. 6,000. H.Paid expenses of different types for Rs. 1,700 in cash. Free AccessBusiness Case GuideClear, practical, in-depth guide to principle-based case building, forecasting, and business case proof. For analysts, decision makers, planners, managers, project leaders—professionals aiming to master the art of “making the case” in real-world business today. Free AccessBusiness Case TemplatesReduce your case-building time by 70% or more. The Integrated Word-Excel-PowerPoint system guides you surely and quickly to professional quality results with a competitive edge. Rely on BC Templates 2021 and win approvals, funding, and top-level support.
Accounting basics for small businesses
Double-entry accounting is a system where every transaction affects at least two accounts. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. Use the basic accounting equation formula to find any missing value of the three, if you know the other two. Firstly, Debit-Credit equality must hold for every event that impacts accounts. The Journal entries in Exhibits 1, 2, and 3 illustrate this equality. Every transaction brings a credit entry in one “account” and an equal, offsetting debit entry in another. Woofer creates a new “account payable” and adds its value to Accounts payable.
- The claims of owners can be realized only after outside creditors’ claims are satisfied.
- Variable costsare any costs you incur that change based on the number of units produced or sold.
- To record the owner’s withdrawal of cash from the business.
- The main use of this equation is for the accurate recording of the balance sheet.
- Interest Payable is the amount of expense that has been incurred but not yet paid.
- We know that every business holds some properties known as assets.
For a company keeping accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of its accounts. The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts.
Final Thoughts On Calculating The Equation
Equityis the portion of the company that actually belongs to the owner. If shareholders own the company, then stockholders’ equity would fall into this category as well. Liabilitiesare obligations that it must pay, including things like lease payments, merchant account fees, accounts payable, and any other debt service. Managing your business’s finances and revenues can be a full-time job, so you may need to create a financial position to handle these duties within your small business. The new corporation received $30,000 cash in exchange for ownership in common stock (10,000 shares at $3 each).
To maintain accuracy, accountants must follow a step by step process of recording entries. The owner’s equity for Public Limited companies also includes shareholder’s equity plus retained earnings.
This provides valuable information to creditors or banks that might be considering a loan application or investment in the company. The basic accounting equation is less detailed than the expanded accounting equation.
- The Integrated Word-Excel-PowerPoint system guides you surely and quickly to professional quality results with a competitive edge.
- It can be defined as the total number of dollars that a company would have left if it liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities.
- Examples of liabilities are accounts payable, short-term debt borrowings, and long-term debts.
- Obligations owed to other companies and people are considered liabilities and can be categorized as current and long-term liabilities.
- For every transaction, at least two classes of accounts are impacted.
- Your assets include your valuable resources, while your liabilities include any debts or obligations you owe.
- Double-entry accounting is the practice where one transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation.
The value of liabilities also keeps on changing from time to time. An increase in the value of liabilities means that the firm has to pay more and a decrease in the value suggests that the firm has to pay less. An asset is a resource that is owned or controlled by the company to be used for future benefits. Some assets are tangible like cash while others are theoretical or intangible like goodwill or copyrights.
If assets increase, either liabilities or owner’s equity must increase to balance out the equation. The opposite is true if liabilities or equity increase. The equation is generally written with liabilities appearing before owner’s equity because creditors usually have to be repaid before investors in a bankruptcy. In this sense, the liabilities are considered more current than the equity. This is consistent with financial reporting where current assets and liabilities are always reported before long-term assets and liabilities.
What Is Shareholders’ Equity in the Accounting Equation?
This equation should be supported by the information on a company’s balance sheet. On your balance sheet, these three components will show how your business is financially operating. Your assets include your valuable resources, while your liabilities include any debts or obligations you owe. If your assets are financed by debt, it’ll be listed as a liability on your balance sheet.
If a business has $1,000 of assets and $500 of liabilities the $500 of liabilities are, in effect, a claim on the assets. Equity is the difference between the assets and liabilities, or $500.
When John sets up his business, assets will increase by $5,000, while the owner’s equity will increase by $5,000. The left side of the T Account shows a debit balance while the right side of the T account shows a credit balance. Account classes such as Assets & Expenses tend to have a debit balance, while account classes such as liabilities & income have a credit balance.
The business’s balance sheet is at the end of the section. The dollar amount of assets on the left side of the equation must equal the sum of liabilities and equity on the right side of the equation. Below are some of the most common accounting equations businesses should know. An accounting transaction is a business Basic accounting equation activity or event that causes a measurable change in the accounting equation. Merely placing an order for goods is not a recordable transaction because no exchange has taken place. In the coming sections, you will learn more about the different kinds of financial statements accountants generate for businesses.
In this article, we discuss the basic accounting equation, explain when to use it, what it includes and offer examples of how it should be listed on balance sheets and income statements. On the other hand, the accounting equation reveals the relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity. This fundamental element of the balance sheet helps companies determine if they have enough funds for operations or expansion as well as how much debt they have. This version of the accounting equation shows the relationship between shareholder’s equity and debt. The shareholder’s equity is what remains after all liabilities are subtracted. Creditors, or the people who lend money, are the ones who have the first claim to a company’s assets.
By ensuring that these three elements balance, accountants can make sure that the financial statements are correct. The accounting equation is important because it forms the foundation for all financial statements. The income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows can all be derived from this one simple equation. Furthermore, the accounting equation helps to ensure that a company’s financial statements are accurate. The balance sheet shows the assets, liabilities & owners’ equity.

